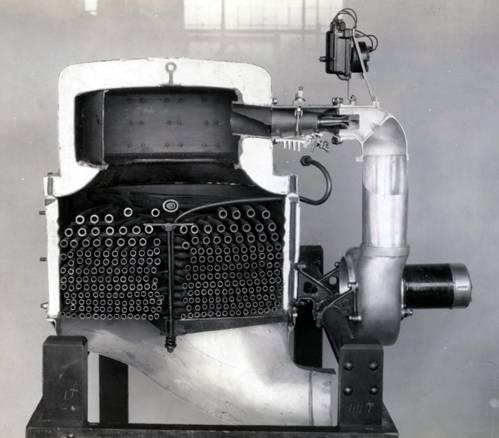
 Doble Water Tube Boiler
(monotube)
Doble Steam Motors automobiles, built from 1924-1931, are considered by many to be the finest steam
vehicles ever produced, with the boiler figuring significantly in this evaluation. An electric fan and
igniter made the burner faster and easier to start and the small volume of fluid in the water tube boiler
reached operating temperature and pressure in much less time than the Stanley. Doble images
The Doble is a once-through boiler, water entering one end and heat applied until emerging from the
other as steam in contrast to recirculating boilers which cycle water endlessly through a heating loop,
extracting only that portion converted to steam. The Doble is also a monotube boiler, meaning there is
only one tube for the water to pass through rather than a number of parallel tubes.
*
The small water volume provides
little reserve power in excess of
maximum steady state output.
*
Superheating in a tube only starts
above the water level; minor level
fluctuation changes the length of the
portions generating and
superheating steam, making
accurate control difficult.
*
The peak firing rate is limited by
DNB and a circulation ratio of 1.
Notwithstanding the above tradeoffs, monotube boilers have been the favored steam car boiler for
generations and only relatively recently are we seeing a shift.
Doble Water Tube Boiler
(monotube)
Doble Steam Motors automobiles, built from 1924-1931, are considered by many to be the finest steam
vehicles ever produced, with the boiler figuring significantly in this evaluation. An electric fan and
igniter made the burner faster and easier to start and the small volume of fluid in the water tube boiler
reached operating temperature and pressure in much less time than the Stanley. Doble images
The Doble is a once-through boiler, water entering one end and heat applied until emerging from the
other as steam in contrast to recirculating boilers which cycle water endlessly through a heating loop,
extracting only that portion converted to steam. The Doble is also a monotube boiler, meaning there is
only one tube for the water to pass through rather than a number of parallel tubes.
*
The small water volume provides
little reserve power in excess of
maximum steady state output.
*
Superheating in a tube only starts
above the water level; minor level
fluctuation changes the length of the
portions generating and
superheating steam, making
accurate control difficult.
*
The peak firing rate is limited by
DNB and a circulation ratio of 1.
Notwithstanding the above tradeoffs, monotube boilers have been the favored steam car boiler for
generations and only relatively recently are we seeing a shift.
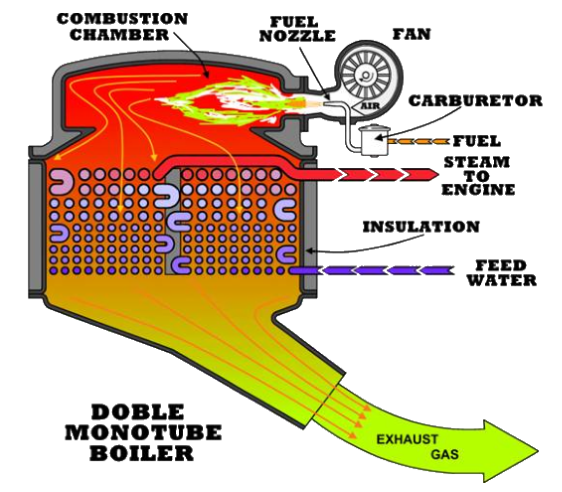
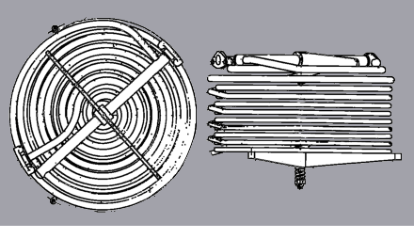



 The Doble monotube is composed of a number of helical ‘pancake’ coils, so named because the tube
windings comprise flat discs stacked upon one another and connected end-to-end. Water entering a
‘pancake’ from the outside spirals inwards until reaching center, moves upwards to the next
‘pancake’ and then spirals outwards. See image of Doble ‘pancake’ coil stack below.
The illustrations show the monotube
growing progressively larger from
entrance to exit; this enlargement serving
to check velocity and resistance buildup as
heating causes the water to expand.
Because the boiler is also drumless (see
what we mean about endless classifications
in steam technology?), it is very safe, the
stored energy in the small volume of water
presenting minimal hazard in the event of a
tube failure. Compared to a fire tube
boiler, there is little water or metal mass to
be heated, allowing the boiler to reach
operating pressure rapidly. The monotube
has its tradeoffs:
The Doble monotube is composed of a number of helical ‘pancake’ coils, so named because the tube
windings comprise flat discs stacked upon one another and connected end-to-end. Water entering a
‘pancake’ from the outside spirals inwards until reaching center, moves upwards to the next
‘pancake’ and then spirals outwards. See image of Doble ‘pancake’ coil stack below.
The illustrations show the monotube
growing progressively larger from
entrance to exit; this enlargement serving
to check velocity and resistance buildup as
heating causes the water to expand.
Because the boiler is also drumless (see
what we mean about endless classifications
in steam technology?), it is very safe, the
stored energy in the small volume of water
presenting minimal hazard in the event of a
tube failure. Compared to a fire tube
boiler, there is little water or metal mass to
be heated, allowing the boiler to reach
operating pressure rapidly. The monotube
has its tradeoffs:
 Doble Water Tube Boiler
(monotube)
Doble Steam Motors automobiles, built from 1924-1931, are considered by many to be the finest steam
vehicles ever produced, with the boiler figuring significantly in this evaluation. An electric fan and
igniter made the burner faster and easier to start and the small volume of fluid in the water tube boiler
reached operating temperature and pressure in much less time than the Stanley. Doble images
The Doble is a once-through boiler, water entering one end and heat applied until emerging from the
other as steam in contrast to recirculating boilers which cycle water endlessly through a heating loop,
extracting only that portion converted to steam. The Doble is also a monotube boiler, meaning there is
only one tube for the water to pass through rather than a number of parallel tubes.
*
The small water volume provides
little reserve power in excess of
maximum steady state output.
*
Superheating in a tube only starts
above the water level; minor level
fluctuation changes the length of the
portions generating and
superheating steam, making
accurate control difficult.
*
The peak firing rate is limited by
DNB and a circulation ratio of 1.
Notwithstanding the above tradeoffs, monotube boilers have been the favored steam car boiler for
generations and only relatively recently are we seeing a shift.
Doble Water Tube Boiler
(monotube)
Doble Steam Motors automobiles, built from 1924-1931, are considered by many to be the finest steam
vehicles ever produced, with the boiler figuring significantly in this evaluation. An electric fan and
igniter made the burner faster and easier to start and the small volume of fluid in the water tube boiler
reached operating temperature and pressure in much less time than the Stanley. Doble images
The Doble is a once-through boiler, water entering one end and heat applied until emerging from the
other as steam in contrast to recirculating boilers which cycle water endlessly through a heating loop,
extracting only that portion converted to steam. The Doble is also a monotube boiler, meaning there is
only one tube for the water to pass through rather than a number of parallel tubes.
*
The small water volume provides
little reserve power in excess of
maximum steady state output.
*
Superheating in a tube only starts
above the water level; minor level
fluctuation changes the length of the
portions generating and
superheating steam, making
accurate control difficult.
*
The peak firing rate is limited by
DNB and a circulation ratio of 1.
Notwithstanding the above tradeoffs, monotube boilers have been the favored steam car boiler for
generations and only relatively recently are we seeing a shift.





 The Doble monotube is composed of a number of helical ‘pancake’ coils, so named because the tube
windings comprise flat discs stacked upon one another and connected end-to-end. Water entering a
‘pancake’ from the outside spirals inwards until reaching center, moves upwards to the next
‘pancake’ and then spirals outwards. See image of Doble ‘pancake’ coil stack below.
The illustrations show the monotube
growing progressively larger from
entrance to exit; this enlargement serving
to check velocity and resistance buildup as
heating causes the water to expand.
Because the boiler is also drumless (see
what we mean about endless classifications
in steam technology?), it is very safe, the
stored energy in the small volume of water
presenting minimal hazard in the event of a
tube failure. Compared to a fire tube
boiler, there is little water or metal mass to
be heated, allowing the boiler to reach
operating pressure rapidly. The monotube
has its tradeoffs:
The Doble monotube is composed of a number of helical ‘pancake’ coils, so named because the tube
windings comprise flat discs stacked upon one another and connected end-to-end. Water entering a
‘pancake’ from the outside spirals inwards until reaching center, moves upwards to the next
‘pancake’ and then spirals outwards. See image of Doble ‘pancake’ coil stack below.
The illustrations show the monotube
growing progressively larger from
entrance to exit; this enlargement serving
to check velocity and resistance buildup as
heating causes the water to expand.
Because the boiler is also drumless (see
what we mean about endless classifications
in steam technology?), it is very safe, the
stored energy in the small volume of water
presenting minimal hazard in the event of a
tube failure. Compared to a fire tube
boiler, there is little water or metal mass to
be heated, allowing the boiler to reach
operating pressure rapidly. The monotube
has its tradeoffs: